VMware Fault Tolerance setup
MX-ONE Service Node running on top of a VMware vSphere HA and FT infrastructure can have a higher level of business continuity than VMware vSphere HA, according to the VMware documentation: “FT provides a higher level of availability, allowing users to protect any virtual machine from a host failure with no loss of data, transactions, or connections. FT provides zero downtime, zero data loss, and continuous availability for your applications”.
When MX-ONE Service Node guest machines are running in a VMware vSphere Fault Tolerance cluster, a transparent failover solution can be achieved. This means that in the event that a physical server where a Service Node guest machine is running goes down, no calls will be dropped during the failover process and continuity will be maintained. This transparent failover is possible, according to VMware, because Fault Tolerance uses VMware vLockstep technology, which guarantees the primary and secondary VMs execute exactly the same x86 instruction sequences. Fault Tolerance requires that the hosts CPUs are compatible with vLockstep technology, which requires additional physical processor extensions.
That is to say when a MX-ONE Service Node guest machine is running in VMware vSphere Fault Tolerance infrastructure, there is an additional Service Node guest machine running in parallel on a different physical server executing the same instructions. In this scenario, the two guest machines are synchronized or mirrored, so that in the case of a primary host server failure, the second parallel virtual machine takes over and becomes the new primary.
The figure below shows a standard MX-ONE composed of two Service Node guest machines running on top of VMware´s FT infrastructure.
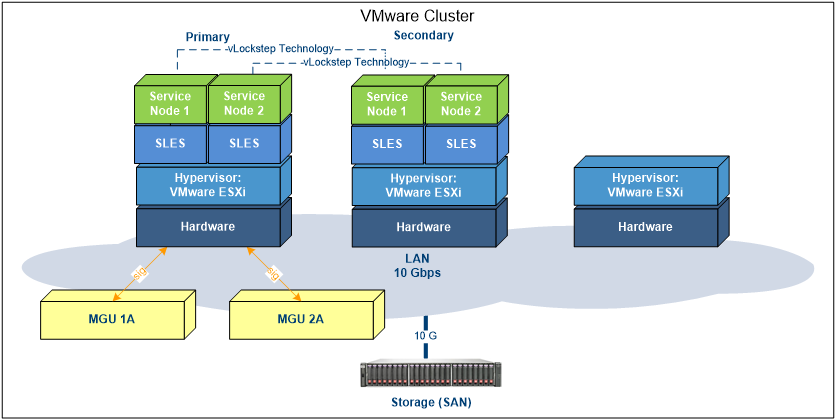
In normal operation, the signaling between Service Node and MGU is transmitted via the “primary physical server”.
To describe this process briefly, when a failure in the primary server hardware occurs, VMware´s mechanism in the secondary server will immediately detect it, take over and start to process pending I/O operations.
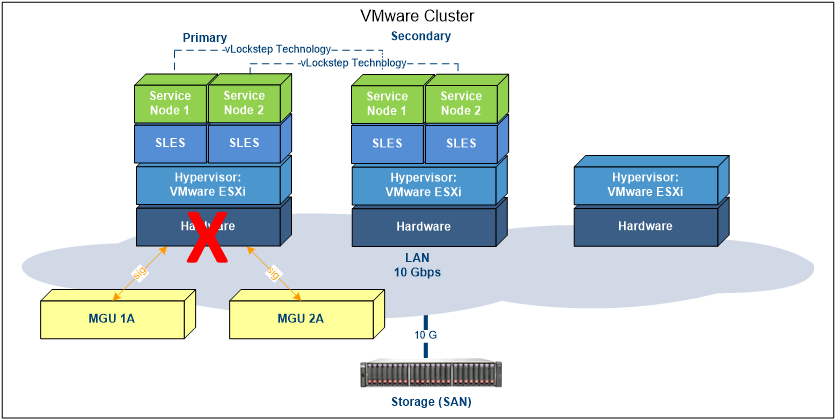
The secondary machine will then perform a “go live” operation and become the new primary server.
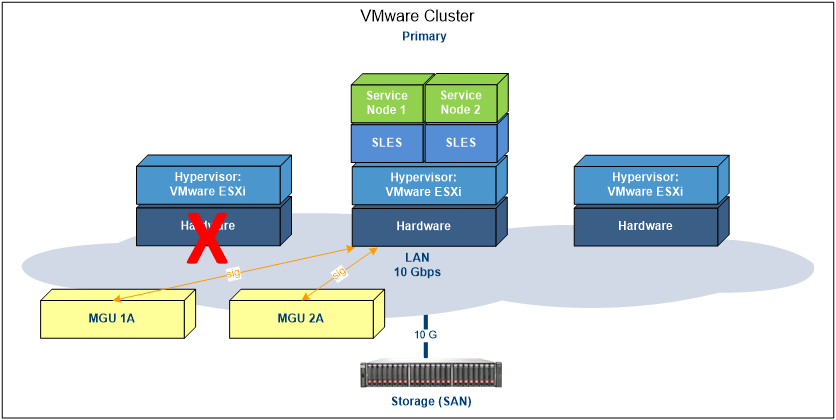
As part of the recovery process, after the secondary machine successfully takes over, VMware´s HA algorithm selects a new host machine in the cluster that is working properly and has available resources to create a new secondary host machine. This is to ensure that the system is protected again in case of a new hardware failure.
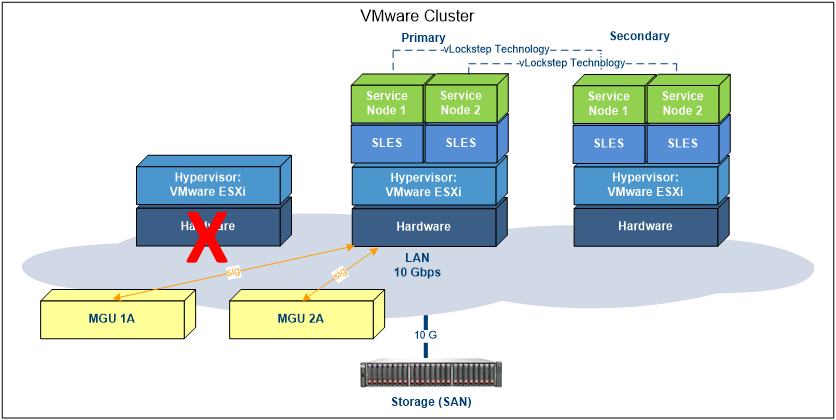
This last process is optional, although highly recommended. It is, of course, possible to limit the cluster to a primary and secondary host. Although, for added security it is always better to have three or more hosts in a cluster to re-establish a full active-active situation within minutes of the initial failure of a primary host.
From the MX-ONE Service Node call manager perspective no server failure is detected. The failover process is handled by VMware´s Fault Tolerance, where the signaling between MX-ONE Service Node and its associated MGUs continue to work normally, although the call processing is maintained by the “secondary physical server” instead. From an end user perspective, the MX-ONE will continue to work normally and ongoing calls and feature requests are maintained. Even from a management continuity perspective there is no loss of functionality, as the database is in a SAN environment, which is shared by the primary and secondary server. This functionality is similar to a hot standby solution. Such a solution can be used by mission critical customers if they desire a more reliable system.
Requirements for VMware Fault Tolerance setup:
- SAN (Storage Area Networks) and Network requirements for High Availability and Fault Tolerance according to VMware specifications
- VMware vSphere, Hypervisor: ESXi 6.7
- VMware vCenter
- VMware VMotion
- VMware High Availability
- VMware Fault Tolerance
It should be noted that a SAN environment and multiple LAN segments are required by VMware in order for this option to be deployed. Refer to the latest VMware packaging options to determine the VMware software editions that best fit the requirements. The VMware vSphere enterprise editions should include HA/FT and VMotion. VMware vCenter is usually ordered separately and required to set this environment in place.
Mitel strongly recommends that partners/customers always check the latest High Availability/FT requirements with a qualified VMware technical representative.
Mitel strongly recommends that the partner/customers read the following VMware´s documents:
About vSphere Availability
https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-vSphere/6.5/com.vmware.vsphere.avail.doc/GUID-63F459B7-8884-4818-8872-C9753B2E0215.html
Providing Fault Tolerance for Virtual Machines
Fault Tolerance Requirements, Limits, and Licensing