Network Configurations and Concepts
The figure in Example 1 below shows one possible network configuration, where all involved parties are located in different MX-ONE, but of course, the parties can be co-located in the same exchange in any combination. If all parties are located in the same MX-ONE, it is an internal case.
When the customer group function is used, the following descriptions apply to the CCOP with differences:
- Central operator's MX-ONE is replaced by Customer Centralized Operator's MX-ONE.
- Common Channel Signaling (CCS) network is replaced by ISDN network or H.323 network.
Originating MX-ONE
The exchange where the incoming public call enters the ISDN or H.323 network, that is, the signaling protocol changes, so it is also a gateway exchange. If the call originates from an internal party in the ISDN network, the originating MX-ONE is where that party is located. If the call originates from an internal party in the ISDN or H.323 network, it must never be rerouted.
Terminating MX-ONE
The exchange where the wanted party is located, and where the rerouting is initiated. The wanted party corresponds to the dialed number, or to the called number if, for example, a prior diversion has occurred. This MX-ONE also normally provides the rerouting destination number. The actual rerouting is however executed or controlled by the originating exchange, by setting up a new call from there.
The MX-ONE of a Central Operator
The exchange where the central operator (group) is located.
Private Telephone Network Internal Call
A call which originates and terminates in the Private Telephone Network (PTN), in this context an ISDN, H.323 or (with certain limitations) a SIP network.
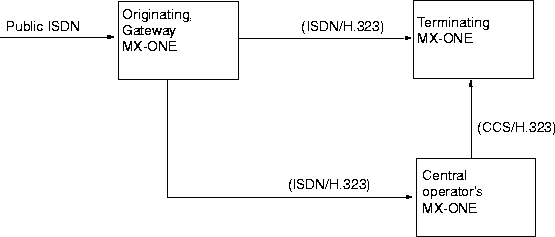
Location Example 1
The wanted party is in an MX-ONE of its own, the terminating MX-ONE, and the Central operator is also in a separate MX-ONE:
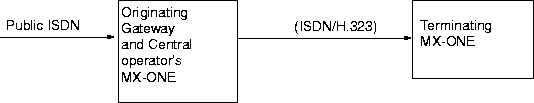
Location Example 2
The Central operator is in the gateway exchange:
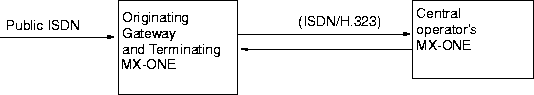
Location Example 3
The wanted party is in the gateway exchange:
Virtual Private Network
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) consists of MX-ONE systems or ASB 501 04 exchanges connected via the public transparent ISDN network. Closed numbering plan (Coordinated numbering plan) is required for VPN.
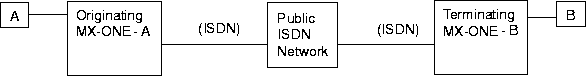
VPN is a service within the public network that makes it possible to establish private calls between the MX-ONE systems that are connected to the public network. For private calls that use the VPN service, the service level is almost the same as for a private network. The network services can be used as in the private network, but the public network may inflict some restrictions.