Echo Canceler (EC)
The Echo Canceler (EC) eliminates the possible echo of send signal from the return signal (see figure below). Echo is normally caused by reflections in transition from 2-to-4 wires, but also acoustic echo in telephones can occur. The EC is only used for calls over packet switched network (VoIP) as depicted in figure below.
There are various configurations of the EC which is described further on as well as in the See Configuration.
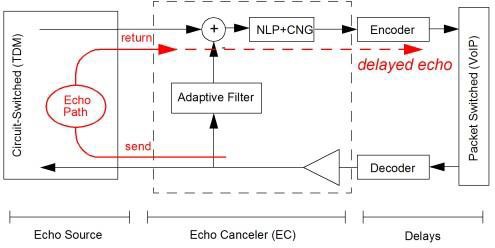
The reason for using EC on VoIP calls is that echo in combination with (long) delays as caused by packet switched network is much more disturbing than echo when there is no or very little delay as can be expected in the circuit switched network (TDM).
The experience of how echo is perceived by the user on the packet side is a sum of echo source, echo canceler operation and packet network delays included delays in media gateways (encoding, decoding, jitter buffers), network (switches and routers) and endpoints (encoding, decoding, jitter buffers).
MGU2 supports two EC types for VoIP GW calls: Standard EC and Dual Filter EC (DFEC). EC type and settings very much impacts the MSP load.
The EC also includes a Non-Linear Processor (NLP), a sub function that is capable of handling non-linear part of residual echo that the linear filter of the EC cannot cancel. By default, NLP is disabled and is only recommended to be enabled when needed.
When NLP is enabled and if engaged, it generates comfort noise (CNG) towards IP. CNG can also be changed to generate silence if CNG is not wanted.