General
An information system can consist of, for example, a message switching system of type interception computer, voice mail system, messaging system, or an ANCD server running on a service node. These operational directions deal with the commands which are common to all types of information systems.
Instructions for specific types of information systems are described in separate operational directions. A factor applying generally to all types of information systems is that they shall be connected to the exchange via the general interface for information systems.
The MESSAGE WAITING function is also included in the general interface for information systems. Message waiting means that when an extension receives a message in an information system, the extension will be notified of this on the telephone.
Notification can take place in the following different ways:
- Ring signal. Ringing is achieved as a single burst (pling) on the bell for an analogue telephone. The period between two plings is 15 minutes (changeable by application system parameter PARNUM=45). If the extension is diverted (direct diversion, follow me, or message diversion), no notification will be given.
- Special dial tone.
- Lamp indication. Applicable only for telephones with a dedicated message waiting lamp and connected to an extension board that is capable of providing message waiting lamp indication. When message waiting is initiated, the lamp on the telephone set is turned on.
An application system parameter (PARNUM=88) makes it possible to choose the type of message waiting indication(s) desired. The parameter can be set to either ring signal or special dial tone. The message waiting indications based on parameter selection for different types of telephones will be as follows (the letters a, b, and c refer to the message waiting indications above):
| Telephone Type | Ring Signal Selected | Special Dial Tone Selected |
|---|---|---|
Analog telephone |
a |
b |
Analog telephone with message waiting lamp |
a |
b and c |
IP extension |
a |
b |
IP extension with message waiting lamp |
a |
b and c |
The NETWORK MESSAGE WAITING function is similar to MESSAGE WAITING function with the following differences:
- only voice mail systems can activate/deactivate network message waiting indication.
- the voice mail systems are located in other exchanges.
- used only in a private network environment. Message waiting indication is sent to the other end via ISDN/H.323 virtual call connection.
The following figure shows the connection of an information system to the exchange.
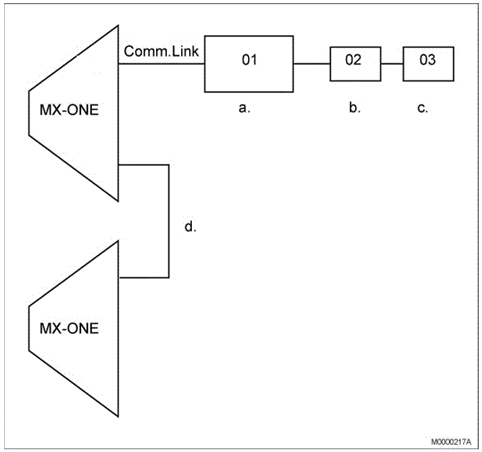
- Directly connected information system with system identity 01
- Indirectly connected information system with system identity 02
- Indirectly connected information system with system identity 03
- Sharing of information system (voice mail system only) with other node within an ISDN/H.323 private network.
The system identity (SID) is used in commands ICMWC and ICMWP.