Interworking with ASB 501 04
For the parameters SIG and VARC, see also the description in section General.
If the cooperating exchange is an ASB 501 04 R4, and ISDN is used, the VARC parameter for full ISDN functionality shall be set to Yes, if network diversion shall be allowed between the exchanges.
If the cooperating exchange is an ASB 501 04 R2/n and ISDN is used, the VARC parameter for full ISDN functionality shall be set to No.
If the cooperating exchange is an ASB 501 04 R4 or ASB 501 04 R2/n, and DPNSS is used, the VARC parameter shall be set to supporting network diversion, if network diversion shall be allowed between the exchanges.
If the cooperating exchange is an ASB 501 04 R1 or earlier release, and DPNSS is used, the VARC parameter shall be set to not supporting network diversion.
In the network configuration below, Node-B and Node-C are connected to PBX-A. PBX-A can, for example, be an ASB 501 04 R1 (or earlier release) using DPNSS, or an ASB 501 04 R2/n using ISDN.
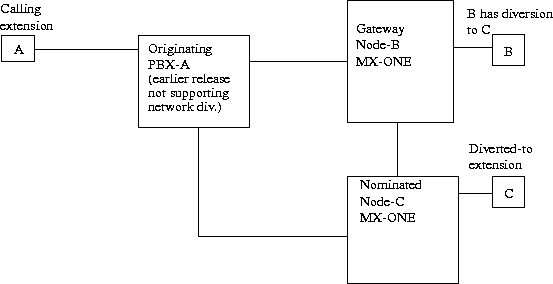
Extension A in originating PBX-A calls extension B. Extension B has activated diversion (that is, any of busy, direct, follow me, or no answer diversion) to extension C in the nominated node.
After A has called extension B, diversion will take place in Node-B. Node-B will in this case act as a gateway exchange. This means that Node-B will continue with a new call set up to extension C in the nominated exchange, that is, for earlier releases it is not possible to use the principle of returning to the originating PBX-A and set up a new call to the nominated Node-C.